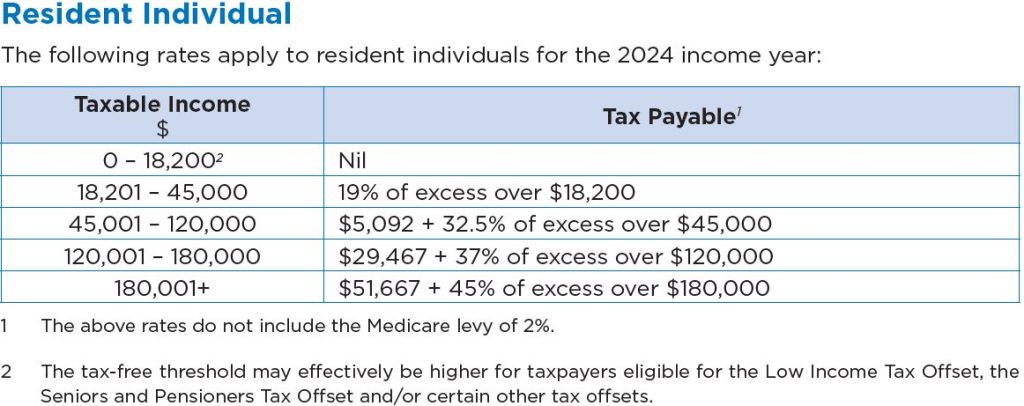
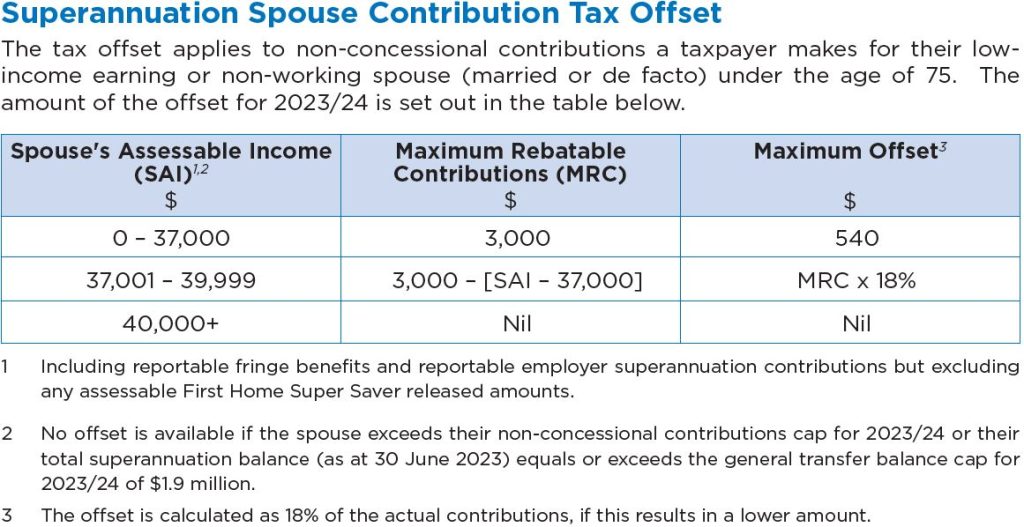
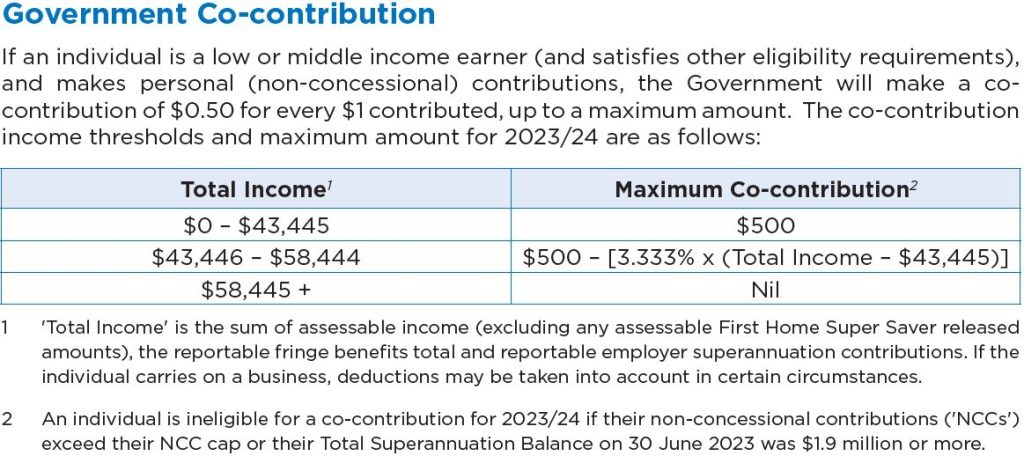
Generally, an Individual is taxed on their income based on a progressive tax system, which means earning a higher level of income will result in having to pay more tax.
In an SMSF, the income is taxed base on whether they are in Accumulation phase or Pension phase and is taxed as follows:
- 15% – Accumulation phase
- 0% – Pension phase
Accumulation Phase
In addition to the income earned by the SMSF, typically there are 3 other ways to add funds into the SMSF which are:
The SMSF pays tax on income at a rate of 15% however, the SMSF generally does not pay tax on Rollovers and Non – Concessional Contributions.
Pension Phase
Benefits in the SMSF are generally paid out in 2 ways:
- Pension payment
- Lump sum payments
In addition to retirement, you can access your Super, so long as you must meet a condition of release.
Tax Rates
Superannuation Warehouse is a specialized SMSF accounting firm however, we are also a Member of the National Tax & Accountants’ Association (NTAA) and as such we have been provided access to detailed information, including tax tables and taxes on various entities. A compilation of the information can be found on the link below:
We have extracted relevant information from the NTAA Booklet available below:
Advantage of an SMSF
One advantage of using a Self-Managed Superannuation Fund (SMSF) is the increased level of control and flexibility it offers in managing your retirement savings. For more information on the benefits of an SMSF, please see the link here.